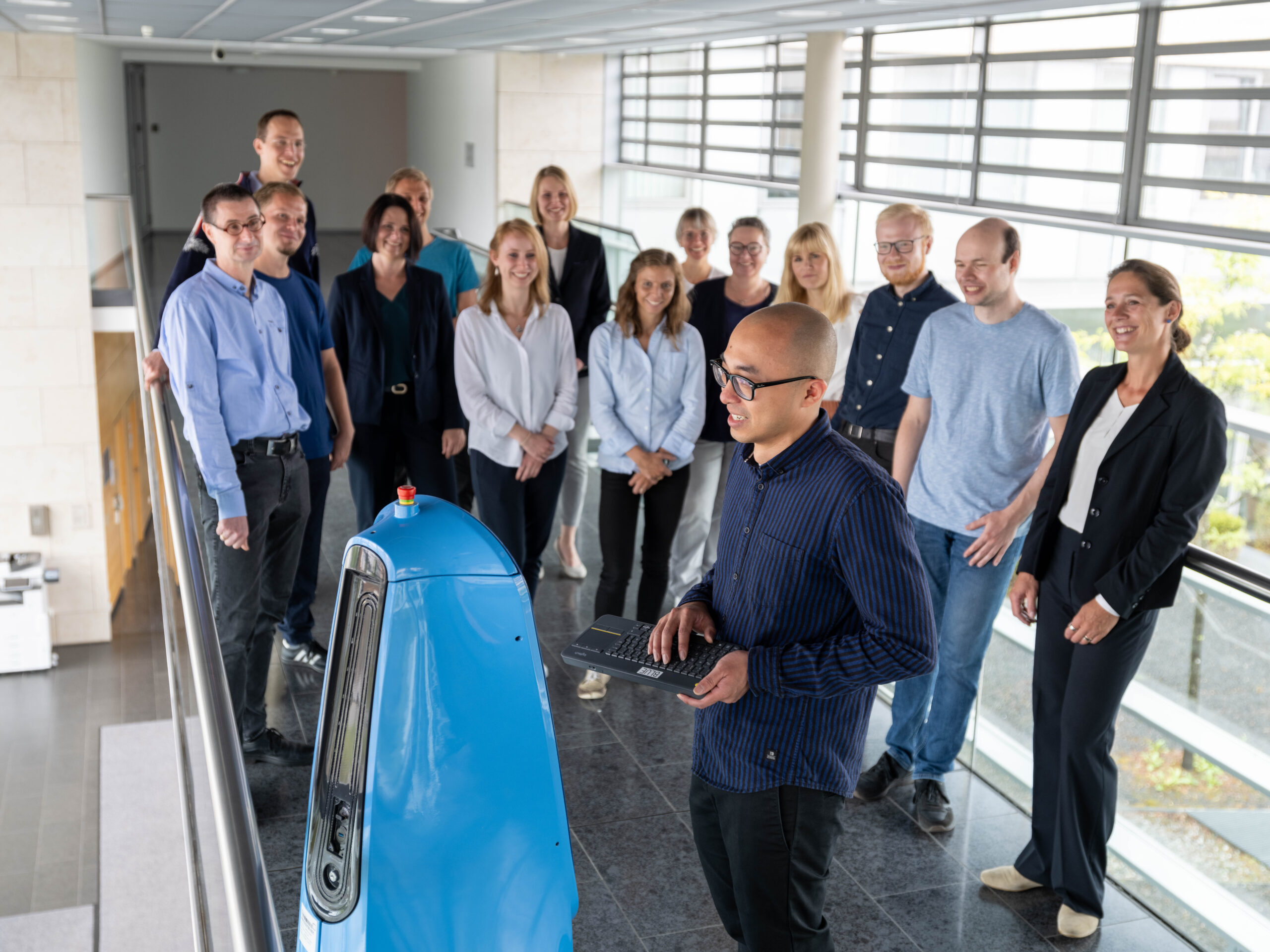
Autonomous training robot for acute and rehabilitation clinics

In addition, we are dedicated to researching and developing new possible fields of application for our therapy robot, such as programmes which assist patients while they practise stair climbing or teach correct weight bearing on the injured leg while walking on crutches.
Furthermore, we are investigating and assessing various navigation methods, technical solutions on how to integrate the robot into the hospital’s own IT infrastructure and in-house emergency call system, as well as a function which would enable the robot to be controlled via the cloud.
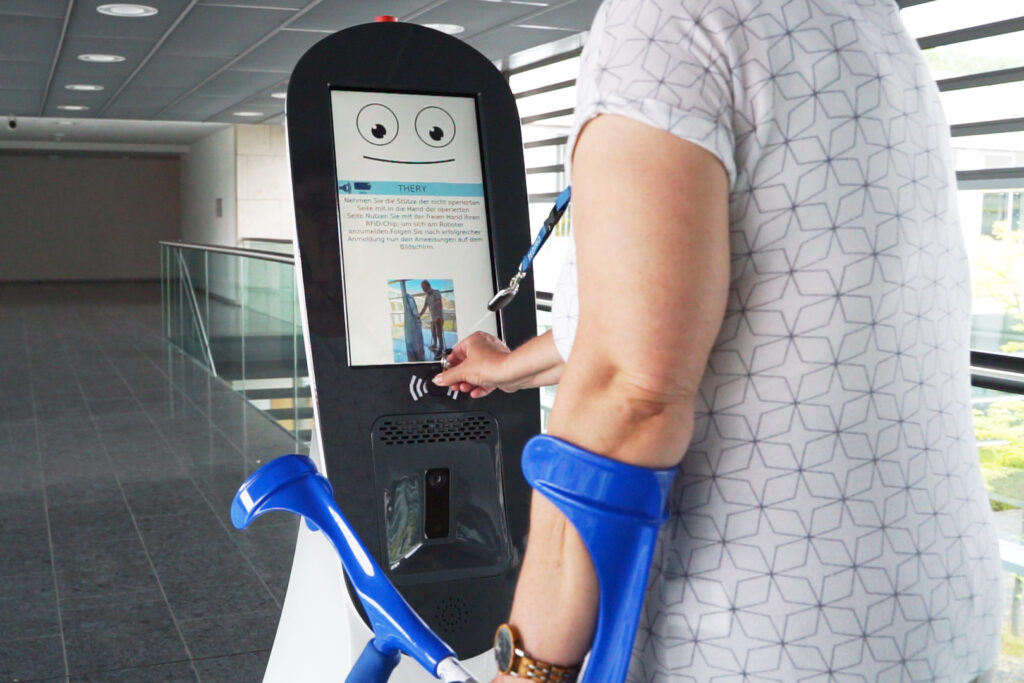
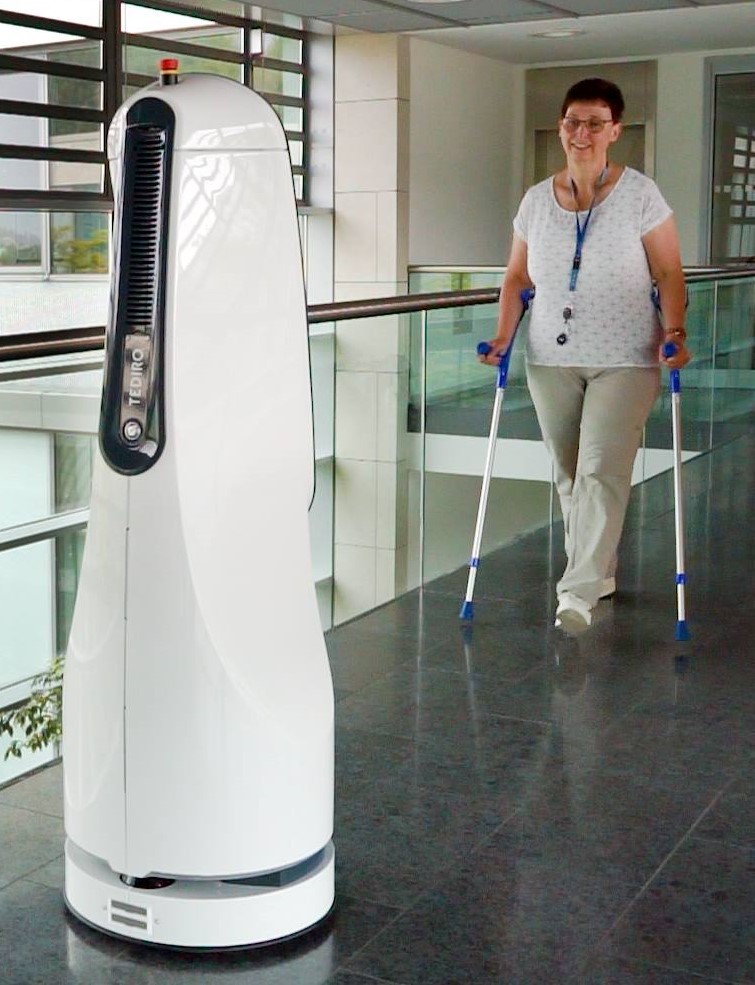
As a first application for the robot, we are working on developing a mobile robot-assisted system to give patients the opportunity to conduct self-directed gait training on crutches, which is intended for use in acute care and rehabilitation clinics/hospitals.
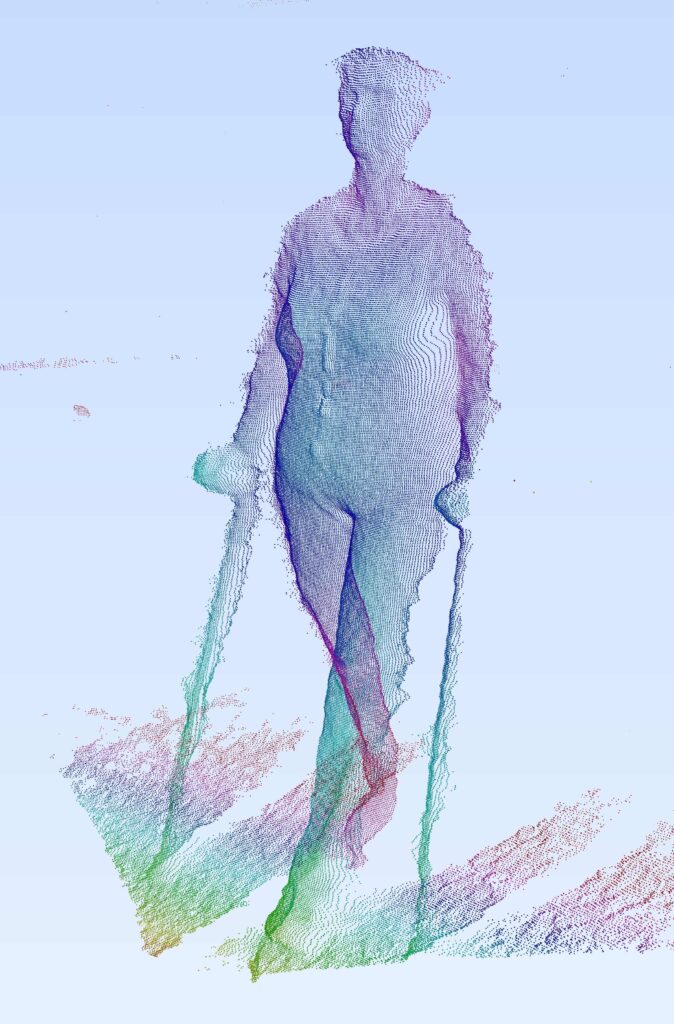
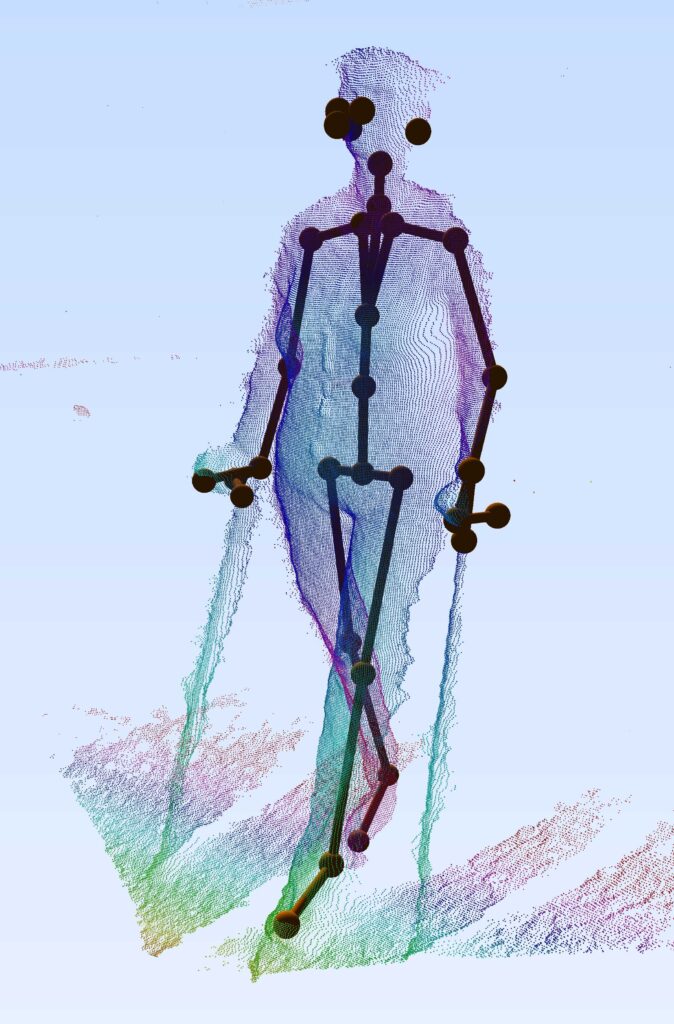
Our robot THERY is based on a mobile robotic platform, which was originally developed for industrial purposes. This platform includes a drive unit and is equipped with a robust robot navigation and safety stack. At TEDIRO, we complement the platform with depth cameras, implement our own software and assemble the housing. In order to enhance the robot-patient interaction during training sessions, the robot has a virtual face, displays correction recommendations on its big screen and features a voice output system.